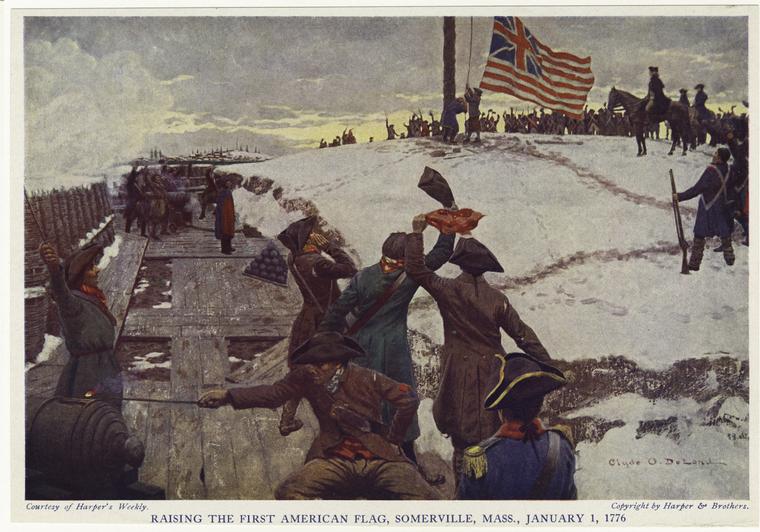

“Raising the first American flag, Somerville, Mass., January 1, 1776.” Harper’s Weekly painting by Clyde Osmer DeLand, 1897. From the digital collections of the New York Public Library; yes, MFB has used this painting before. I like it.
One problem with January’s flag flying dates is that if I snooze a little, you miss a lot. There are four flag-flying dates in the first five days of January: New Year’s Day and statehood days for Georgia, Alaska and Utah. You, Dear Reader, are alert and won’t let any of those dates pass unmarked if you’re in those states, right?
There are more dates to go in January, including New Mexico’s statehood. We’re not halfway done, yet.
President Joe Biden declared flags should fly at half-staff in honor of the late President Jimmy Carter, for 30 days, until January 28. That covers all the dates in the usual flag-flying calendar. When flying flags at half staff, the flag should be hoisted quickly to full staff, then lowered soberly (slowly) to half staff.
In January 2026, the U.S. Flag Code urges citizens to fly flags on these dates, listed chronologically:
- New Year’s Day, January 1, a federal holiday
- January 2, Georgia Statehood Day
- January 3, Alaska Statehood Day
- January 4, Utah Statehood Day
- January 6, New Mexico Statehood Day
- January 9, Connecticut Statehood Day
- Martin Luther King’s Birthday, a federal holiday on the third Monday of January; that date is January 19, in 2026; King’s actual birthday is January 15, and you may fly your flag then, too
- January 26, Michigan Statehood Day
- January 29, Kansas Statehood Day
It will be interesting to some to see whether the White House issues a proclamation to fly the flag on Martin Luther King’s birthday.
You may fly your flag any other day you wish, too; flags should not be flown after sundown unless they are specially lighted, or at one of the few places designated by Congress or Presidential Proclamation for 24-hour flag flying. According to Wikipedia’s listing, those sites include:
- Fort McHenry, Baltimore, Maryland (Presidential Proclamation No. 2795, July 2, 1948).
- Flag House Square, Albemarle and Pratt Streets, Baltimore, Maryland (Public Law 83-319, approved March 26, 1954).
- Marine Corps War Memorial (Iwo Jima Memorial), Arlington, Virginia (Presidential Proclamation No. 3418, June 12, 1961).
- Lexington Battle Green, Lexington, Massachusetts (Public Law 89-335, approved November 8, 1965).
- White House, Washington, D.C. (Presidential Proclamation No. 4000, September 4, 1970).
- Washington Monument, Washington, D.C. (Presidential Proclamation No. 4064, July 6, 1971, effective July 4, 1971).
- Any port of entry to the United States which is continuously open (Presidential Proclamation No. 413 1, May 5, 1972).
- Grounds of the National Memorial Arch in Valley Forge State Park, Valley Forge, Pennsylvania (Public Law 94-53, approved July 4, 1975).

Flag House in 1936, where Mary Pickersgill sewed the garrison-sized, 15-star flag that flew over Fort McHenry at the Battle of Baltimore in 1814; one of the sites where the U.S. flag may be flown 24 hours. The house is at 844 East Pratt & Albemarle Streets (Baltimore, Independent City, Maryland). Cropped image courtesy of the federal HABS—Historic American Buildings Survey of Maryland.
Save




 Posted by Ed Darrell
Posted by Ed Darrell 










