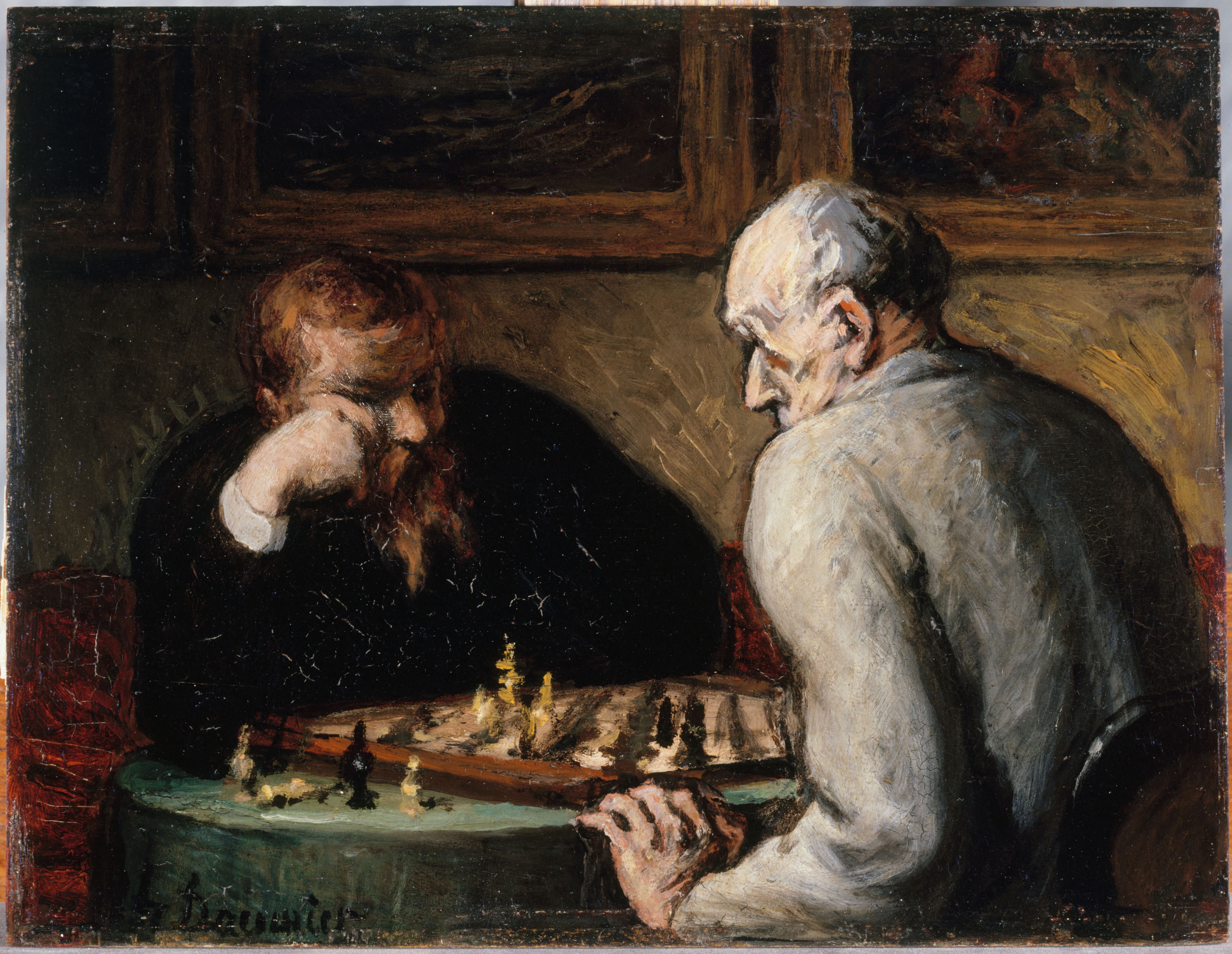
Interesting contrasts, at least.
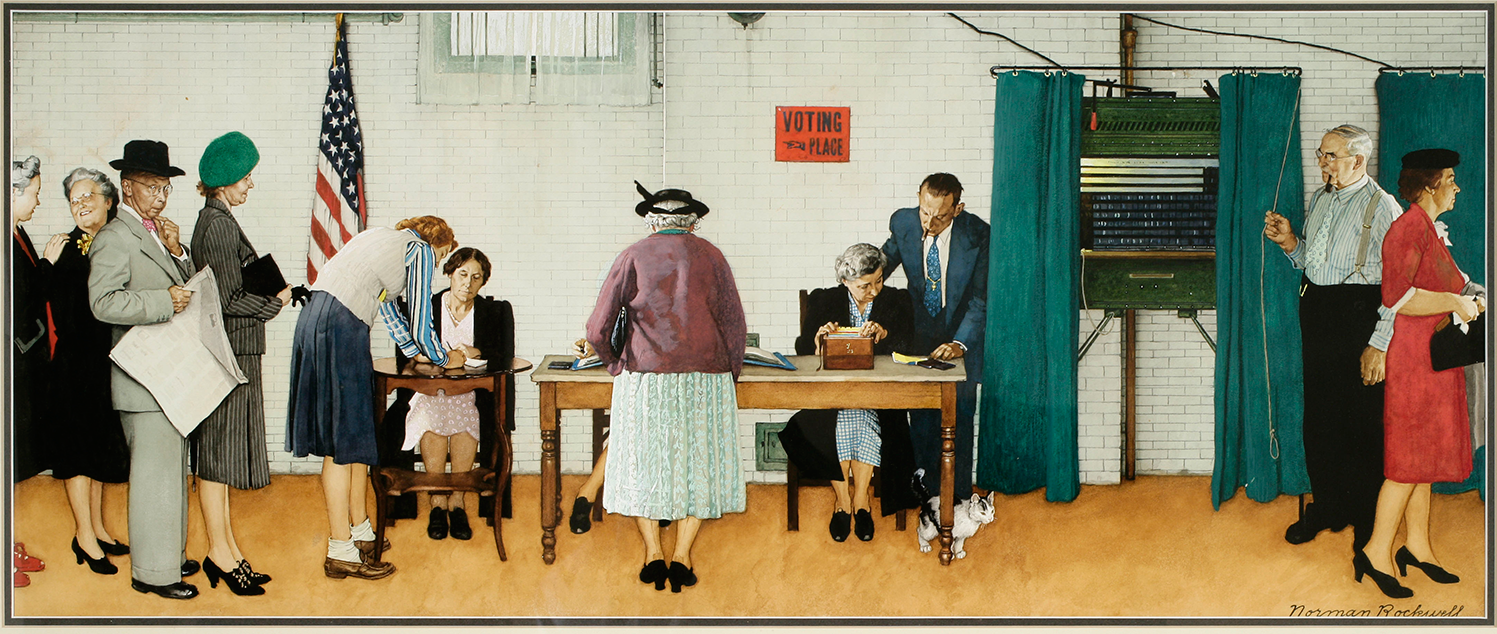
I love the “County Election” painting of George Caleb Bingham, showing an election in 1852, the year incumbent President Millard Fillmore could not get even the nomination of his party. I love the tension of Norman Rockwell’s painting of the 1944 election in Cedar Rapids, Iowa, with tensions we see only in retrospect. (That post also shows real tensions in a family, in the election of 1948, in another Rockwell painting).
What else does the world of art show about elections in America? What do you think?

Illustration from Harper’s Weekly, November 7, 1857, showing election persuasion at the polls – politicians trying to buy votes. Library of Congress collection
If bribery didn’t work, there was always plain old fisticuffs.

Fighting at the polls. Illustration from Harper’s Weekly, November 7, 1857. Library of Congress collections
Here’s an unusual ritual, portrayed about the 1892 contest between William Henry Harrison and Grover Cleveland. Did this really happen? Did the loser pull the winner on a cart through the city?
Louis Dalrymple noted a twist on the tradition four years later.

Puck Magazine, November 11, 1896. “Print shows a bloated businessman holding an American flag labeled ‘Victory,’ riding in a wheelbarrow being pushed by another man; in the background, a young boy is telling a stranger that his Dad had a bet with the other man regarding the outcome of the presidential election. The stranger is uncertain who lost the bet.” Drawing by Louis Dalrymple for Puck. Library of Congress collections
Not sure how long that tradition of the loser pushing or pulling the winner hung on, but by 1904 election night was an occasion to walk about, socialize, and watch fireworks, if this print from the William Randolph Hearst organization is accurate. Teddy Roosevelt won the presidency on his own that year.

“Election night illumination at the Flatiron Building [New York City].” New York Sunday American & Journal, a Hearst newspaper. Library of Congress collections

“Politics in the Oyster House,” 1848 by Richard Caton Woodville. Image found at Wikiwand
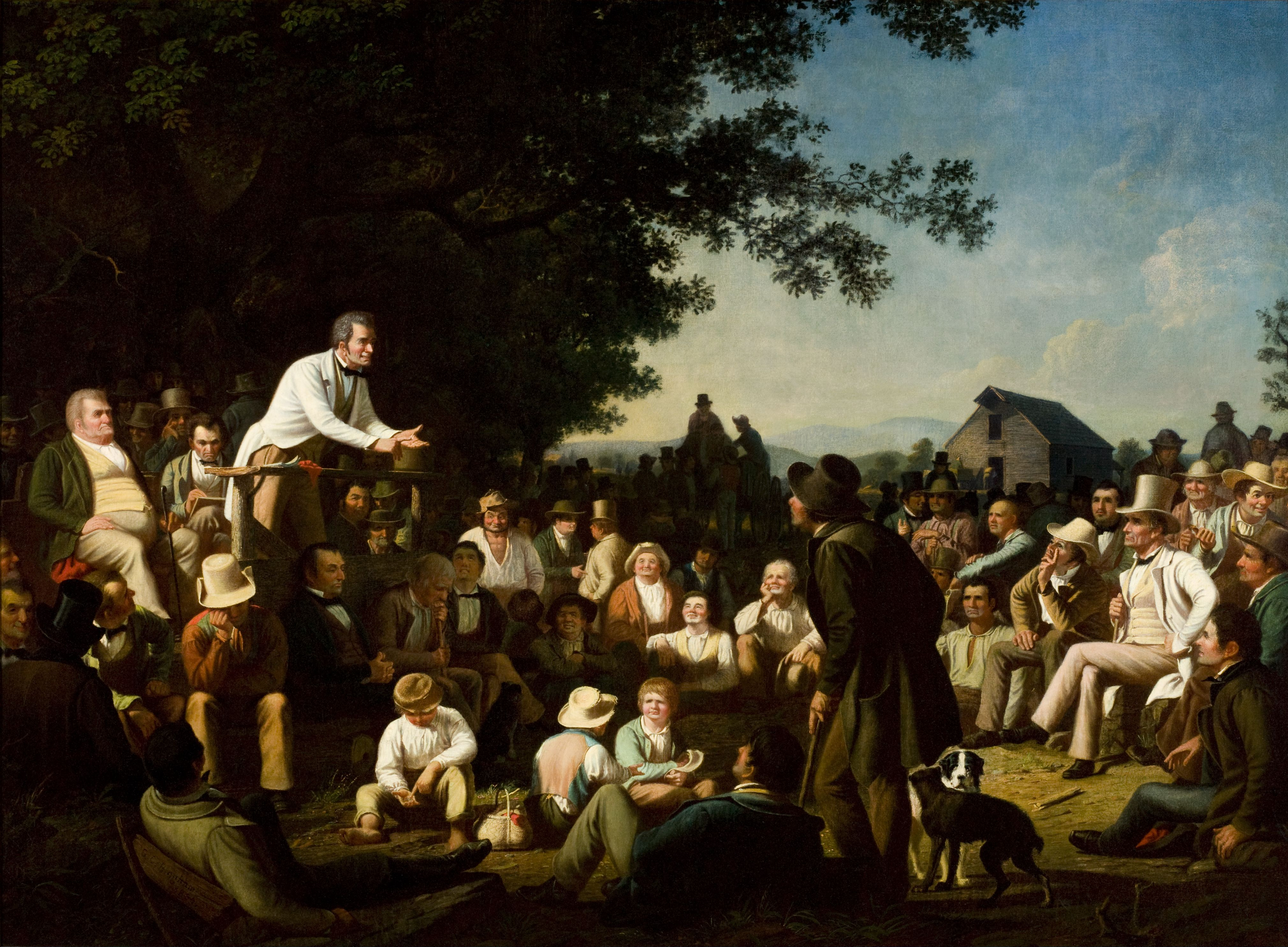

George Caleb Bingham’s “Stump Speaking,” 1853-54. Image from Wikiwand
Not all election work involves a crowd.

George Caleb Bingham, “Canvassing the Vote”

George Caleb Bingham, “The Verdict of the People,” 1854-55. Wikiwand image
This looks more like the campaign party of a victorious candidate in the late 20th and early 21st centuries, though I’m not really sure this tradition survived much past the 2000 election.

John Sloan, “Election Night,” 1907, an image from a New York drinking establishment. Collection of the Memorial Art Gallery of the University of Rochester.
Janie Price’s Evolution of American Painting said:
Here is the scene of Election Night written in Sloan’s Journal:
“Took a walk in the afternoon and saw boys in droves, foraging for fuel for their election fires this evening. . . . after dinner . . . out again and saw the noisy trumpet blowers, confetti throwers and the “ticklers” in use—a small feather duster on a stick which is pushed in the face of each girl by the men, and in the face of men by the girls. A good humorous crowd, so dense in places that it is impossible to control one’s movement.” (John French Sloan)
Women voted for the first time nationwide in 1920, after the ratification of the 19th Amendment. J. F. Kernan’s painting for The Country Gentleman magazine in 1922 shows some of the tensions that remained after the national amendment.

J. F. Kernan in Country Gentleman magazine, November 4, 1922. Wikimedia image
Rockwall made great use of his time and photographs in Cedar Rapids. In addition to the painting there, he used the setting for his famous “Undecided,” which became the cover of the Saturday Evening Post. 1944 was the last time prior to 2016 that both major candidates came from New York.

“Undecided,” Norman Rockwell, 1944. Copyright Curtis Publications
One might wonder if Rockwell considered himself undecided, when one sees this “son” of the painting, from 1960, featuring Rockwell in the same voting booth.

“Norman Rockwell at the Voting Booth” painted in 1960, based on his 1944 studies in Cedar Rapids, it seems to me. Image from The Easel
One last Rockwell to close out, one of my favorites, showing the happy candidate Casey, after having gotten the news that the voters were not so happy with him.

Norman Rockwall, “Elect Casey,” or “Before and After,” November 1958 for the Saturday Evening Post.
Legendary election jokester Dick Tuck once ran for the state legislature in California, on the slogan, “The job needs Tuck, and Tuck needs the job.” He lost, and he said what I can imagine the fictional Casey saying, “The people have spoken. The bastards!”
What are your favorite election day images? What are your memories of elections past?
Spread the word; friends don't allow friends to repeat history.




 Posted by Ed Darrell
Posted by Ed Darrell 








:origin()/pre00/8ed4/th/pre/i/2016/001/6/8/famous_composers_on_mt_rushmore_by_gagambo-d9mbfls.jpg)



































