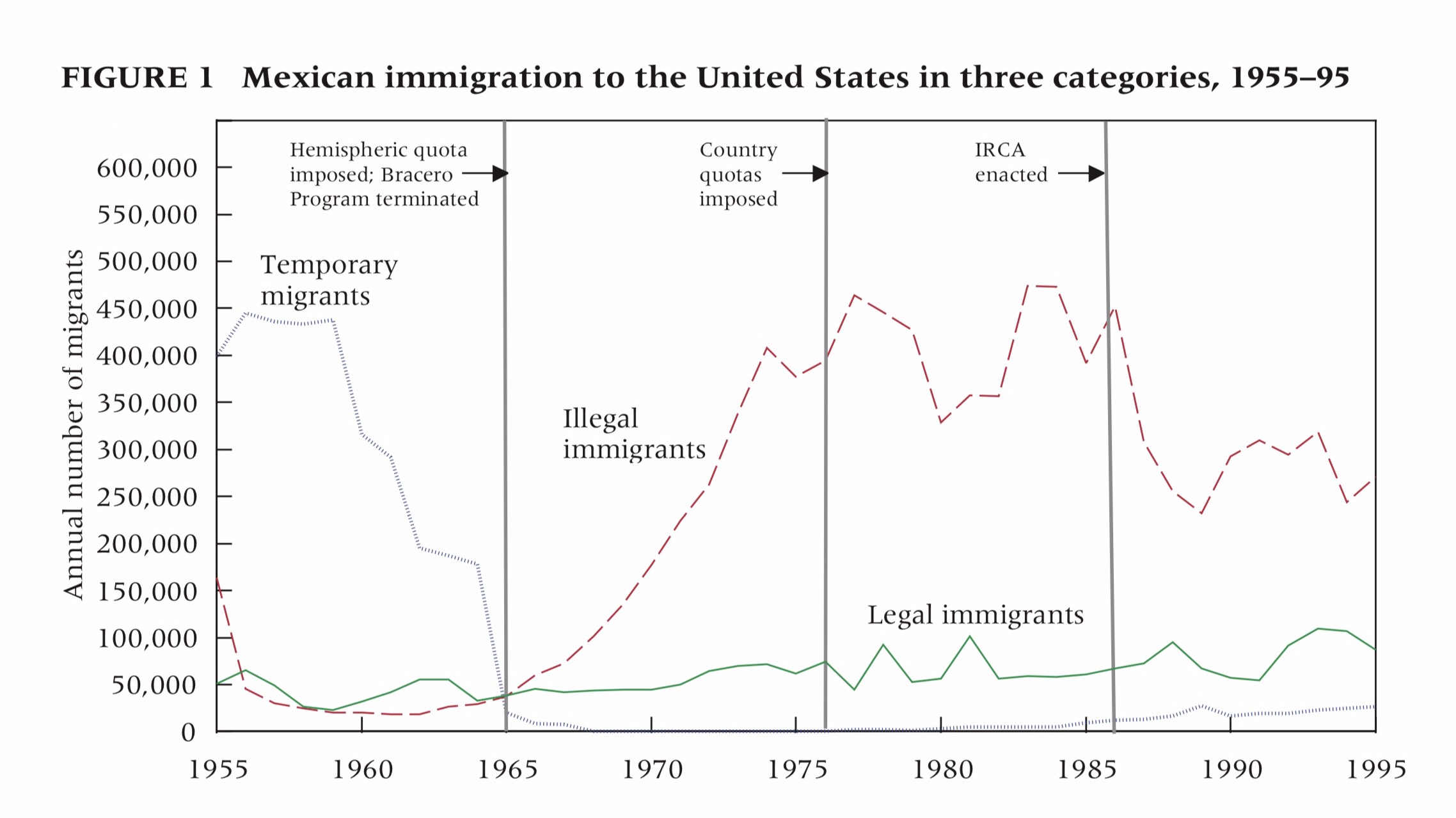
“People don’t grasp the short-term consequences of saving the planet.” Cartoon by Pat Chappatte @PatChappatte, New York Times Syndicate.
From CleanTechnica.com (with additional information added here from the House of Representatives official site):
116TH CONGRESS
1ST SESSION H. RES. 109
Recognizing the duty of the Federal Government to create a Green New Deal.
IN THE HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES
Ms. OCASIO-CORTEZ (for herself, Mr. Hastings, Ms. Tlaib, Mr. Serrano, Mrs. Carolyn B. Maloney of New York, Mr. Vargas, Mr. Espaillat, Mr. Lynch, Ms. Velázquez, Mr. Blumenauer, Mr. Brendan F. Boyle of Pennsylvania, Mr. Castro of Texas, Ms. Clarke of New York, Ms. Jayapal, Mr. Khanna, Mr. Ted Lieu of California, Ms. Pressley, Mr. Welch, Mr. Engel, Mr. Neguse, Mr. Nadler, Mr. McGovern, Mr. Pocan, Mr. Takano, Ms. Norton, Mr. Raskin, Mr. Connolly, Mr. Lowenthal, Ms. Matsui, Mr. Thompson of California, Mr. Levin of California, Ms. Pingree, Mr. Quigley, Mr. Huffman, Mrs. Watson Coleman, Mr. García of Illinois, Mr. Higgins of New York, Ms. Haaland, Ms. Meng, Mr. Carbajal, Mr. Cicilline, Mr. Cohen, Ms. Clark of Massachusetts, Ms. Judy Chu of California, Ms. Mucarsel-Powell, Mr. Moulton, Mr. Grijalva, Mr. Meeks, Mr. Sablan, Ms. Lee of California, Ms. Bonamici, Mr. Sean Patrick Maloney of New York, Ms. Schakowsky, Ms. DeLauro, Mr. Levin of Michigan, Ms. McCollum, Mr. DeSaulnier, Mr. Courtney, Mr. Larson of Connecticut, Ms. Escobar, Mr. Schiff, Mr. Keating, Mr. DeFazio, Ms. Eshoo, Mrs. Trahan, Mr. Gomez, Mr. Kennedy, and Ms. Waters) submitted the following resolution; which was referred to the Committee on Committee on Energy and Commerce, and in addition to the Committees on Science, Space, and Technology, Education and Labor, Transportation and Infrastructure, Agriculture, Natural Resources, Foreign Affairs, Financial Services, the Judiciary, Ways and Means, and Oversight and Reform, for a period to be subsequently determined by the Speaker, in each case for consideration of such provisions as fall within the jurisdiction of the committee concerned.
RESOLUTION
Recognizing the duty of the Federal Government to create
a Green New Deal.
Whereas the October 2018 report entitled ‘‘Special Report on Global Warming of 1.5ºC’’ by the intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change and the November 2018 Fourth National Climate Assessment report found that—
- human activity is the dominant cause of observed climate change over the past century;
- a changing climate is causing sea levels to rise and an increase in wildfires, severe storms, droughts, and other extreme weather events that threaten human life, healthy communities, and critical infrastructure
- global warming at or above 2 degrees Celsius beyond preindustrialized levels will cause—
- mass migration from the regions most affected by climate change;
- more than $500,000,000,000 in lost annual economic output in the United States by the year
2100;
- wildfires that, by 2050, will annually burn at least twice as much forest area in the western
United States than was typically burned by wildfires in the years preceding 2019;
- a loss of more than 99 percent of all coral reefs on Earth;
- more than 350,000,000 more people to be exposed globally to deadly heat stress by 2050; and
- a risk of damage to $1,000,000,000,000 of public infrastructure and coastal real estate in the
United States; and
- global temperatures must be kept below 1.5 degrees Celsius above preindustrialized levels to avoid the most severe impacts of a changing climate, which will require—
- global reductions in greenhouse gas emissions from human sources of 40 to 60 percent from
2010 levels by 2030; and
- net-zero emissions by 2050;
Whereas, because the United States has historically been responsible for a disproportionate amount of greenhouse gas emissions, having emitted 20 percent of global greenhouse gas emissions through 2014, and has a high technological capacity, the United States must take a leading role in reducing emissions through economic transformation;
Whereas the United States is currently experiencing several related crises, with—
- life expectancy declining while basic needs, such as clean air, clean water, healthy food, and adequate health care, housing, transportation, and education, are inaccessible to a significant portion of the United States population;
- a 4-decade trend of economic stagnation, deindustrialization, and antilabor policies that has led
to—
- hourly wages overall stagnating since the 1970s despite increased worker productivity;
- the third-worst level of socioeconomic mobility in the developed world before the Great Recession
- the erosion of the earning and bargaining power of workers in the United States; and
- inadequate resources for public sector workers to confront the challenges of climate change
at local, State, and Federal levels; and
- the greatest income inequality since the 1920s, with—
- the top 1 percent of earners accruing 91percent of gains in the first few years of economic
recovery after the Great Recession;
- a large racial wealth divide amounting to a difference of 20 times more wealth between the average White family and the average Black family; and
- a gender earnings gap that results in women earning approximately 80 percent as much
as men, at the median;
Whereas climate change, pollution, and environmental destruction have exacerbated systemic racial, regional, social, environmental, and economic injustices (referred to in this preamble as ‘‘systemic injustices’’) by disproportionately affecting indigenous communities, communities of color, migrant communities, deindustrialized communities, depopulated rural communities, the poor, low-income workers, women, the elderly, the unhoused, people with disabilities, and youth (referred to in this preamble as ‘‘frontline and vulnerable communities’’);
Whereas, climate change constitutes a direct threat to the national security of the United States—
- by impacting the economic, environmental, and social stability of countries and communities around the world; and
- by acting as a threat multiplier;
Whereas the Federal Government-led mobilizations during World War II and the New Deal created the greatest middle class that the United States has ever seen, but many members of frontline and vulnerable communities were excluded from many of the economic and societal benefits of those mobilizations; and
Whereas the House of Representatives recognizes that a new national, social, industrial, and economic mobilization on a scale not seen since World War II and the New Deal is a historic opportunity—
- to create millions of good, high-wage jobs in the United States;
- to provide unprecedented levels of prosperity and economic security for all people of the United States; and
- to counteract systemic injustices:
Now, therefore, be it
Resolved, That it is the sense of the House of Representatives that—
- it is the duty of the Federal Government to create a Green New Deal—
- to achieve net-zero greenhouse gas emissions through a fair and just transition for all communities and workers;
- to create millions of good, high-wage jobs and ensure prosperity and economic security for all people of the United States;
- to invest in the infrastructure and industry of the United States to sustainably meet the challenges of the 21st century;
- to secure for all people of the United States for generations to come—
(i) clean air and water;
(ii) climate and community resiliency;
(iii) healthy food;
(iv) access to nature; and
(v) a sustainable environment; and
- to promote justice and equity by stopping current, preventing future, and repairing historic oppression of indigenous communities, communities of color, migrant communities, deindustrialized communities, depopulated rural communities, the poor, low-income workers, women, the elderly, the unhoused, people with disabilities, and youth (referred to in this resolution as ‘‘frontline and vulnerable communities’’);
- the goals described in subparagraphs of paragraph (1) above (referred to in this
resolution as the ‘‘Green New Deal goals’’) should be accomplished through a 10-year national mobilization (referred to in this resolution as the ‘‘Green New Deal mobilization’’) that will require the following goals and projects—
- building resiliency against climate change-related disasters, such as extreme weather, including by leveraging funding and providing investments for community-defined projects and strategies;
- repairing and upgrading the infrastructure in the United States, including—
(i) by eliminating pollution and greenhouse gas emissions as much as technologically feasible;
(ii) by guaranteeing universal access to clean water;
(iii) by reducing the risks posed by flooding and other climate impacts; and
(iv) by ensuring that any infrastructure bill considered by Congress addresses climate change;
- meeting 100 percent of the power demand in the United States through clean, renewable, and zero-emission energy sources, including—
(i) by dramatically expanding and upgrading existing renewable power sources; and
(ii) by deploying new capacity;
- building or upgrading to energy-efficient, distributed, and ‘‘smart’’ power grids, and working to ensure affordable access to electricity;
- upgrading all existing buildings in the United States and building new buildings to achieve maximal energy efficiency, water efficiency, safety, affordability, comfort, and durability, including through electrification;
- spurring massive growth in clean manufacturing in the United States and removing pollution and greenhouse gas emissions from manufacturing and industry as much as is technologically feasible, including by expanding renewable energy manufacturing and investing in existing manufacturing and industry;
- working collaboratively with farmers and ranchers in the United States to eliminate pollution and greenhouse gas emissions from the agricultural sector as much as is technologically feasible, including—
(i) by supporting family farming;
(ii) by investing in sustainable farming and land use practices that increase soil health; and
(iii) by building a more sustainable food system that ensures universal access to healthy food;
- overhauling transportation systems in the United States to eliminate pollution and greenhouse gas emissions from the transportation sector as much as is technologically feasible, including through investment in—
(i) zero-emission vehicle infrastructure and manufacturing;
(ii) clean, affordable, and accessible public transportation; and
(iii) high-speed rail;
- mitigating and managing the long-term adverse health, economic, and other effects of pollution and climate change, including by providing funding for community-defined projects and strategies;
- removing greenhouse gases from the atmosphere and reducing pollution, including by restoring natural ecosystems through proven low-tech solutions that increase soil carbon storage, such as preservation and afforestation;
- restoring and protecting threatened, endangered, and fragile ecosystems through locally appropriate and science-based projects that enhance biodiversity and support climate resiliency;
- cleaning up existing hazardous waste and abandoned sites to promote economic development and sustainability;
- identifying other emission and pollution sources and creating solutions to eliminate them; and
- promoting the international exchange of technology, expertise, products, funding, and services, with the aim of making the United States the international leader on climate action, and to help other countries achieve a Green New Deal;
- a Green New Deal must be developed through transparent and inclusive consultation, collaboration, and partnership with frontline and vulnerable communities, labor unions, worker cooperatives, civil society groups, academia, and businesses; and
- to achieve the Green New Deal goals and mobilization, a Green New Deal will require the following goals and projects—
-
-
- providing and leveraging, in a way that ensures that the public receives appropriate ownership stakes and returns on investment, adequate capital (including through community grants, public banks, and other public financing), technical expertise, supporting policies, and other forms of assistance to communities, organizations, Federal, State, and local government agencies, and businesses working on the Green New Deal mobilization;
- ensuring that the Federal Government takes into account the complete environmental and social costs and impacts of emissions through—
(i) existing laws;
(ii) new policies and programs; and
(iii) ensuring that frontline and vulnerable communities shall not be adversely affected;
- providing resources, training, and high-quality education, including higher education, to all people of the United States, with a focus on frontline and vulnerable communities, so those communities may be full and equal participants in the Green New Deal mobilization;
- making public investments in the research and development of new clean and renewable energy technologies and industries;
- directing investments to spur economic development, deepen and diversify industry in local and regional economies, and build wealth and community ownership, while prioritizing high-quality job creation and economic, social, and environmental benefits in frontline and vulnerable communities that may otherwise struggle with the transition away from greenhouse gas intensive industries;
- ensuring the use of democratic and participatory processes that are inclusive of and led by frontline and vulnerable communities and workers to plan, implement, and administer the Green New Deal mobilization at the local level;
- ensuring that the Green New Deal mobilization creates high-quality union jobs that pay prevailing wages, hires local workers, offers training and advancement opportunities, and guarantees wage and benefit parity for workers affected by the transition;
- guaranteeing a job with a family-sustaining wage, adequate family and medical leave, paid vacations, and retirement security to all people of the United States;
- strengthening and protecting the right of all workers to organize, unionize, and collectively bargain free of coercion, intimidation, and harassment;
- strengthening and enforcing labor, workplace health and safety, antidiscrimination, and wage and hour standards across all employers, industries, and sectors;
- enacting and enforcing trade rules, procurement standards, and border adjustments with strong labor and environmental protections—
(i) to stop the transfer of jobs and pollution overseas; and
(ii) to grow domestic manufacturing in the United States;
- ensuring that public lands, waters, and oceans are protected and that eminent domain is not abused;
- obtaining the free, prior, and informed consent of indigenous people for all decisions that affect indigenous people and their traditional territories, honoring all treaties and agreements with indigenous people, and protecting and enforcing the sovereignty and land rights of indigenous people;
- ensuring a commercial environment where every businessperson is free from unfair competition and domination by domestic or international monopolies; and
- providing all people of the United States with—
(i) high-quality health care;
(ii) affordable, safe, and adequate housing;
(iii) economic security; and
(iv) access to clean water, clean air, healthy and affordable food, and nature.
[End of text]
In the Senate, the companion (and matching) resolution sponsored by Massachusetts Sen. Edward J. Markey is S. Res. 59. It was referred to the Senate Committee on Environment and Public Works (See more information in the Congressional Record, pages S1140-1142. Senate cosponsors are, “Mr. Merkley, Mr. Sanders, Mrs. Gillibrand,
Ms. Harris, Ms. Warren, Ms. Hirono, Mr. Wyden, Mr. Blumenthal, Mr.
Booker, Ms. Klobuchar, and Mr. Murphy.”
More:
- “What’s actually in the ‘Green New Deal’ from the Democrats,” The Fact Checker, Salvador Rizzo, Washington Post, February 11, 2019
- “The Energy 202: Green New Deal is already sparking debate over nuclear energy,” Dino Grandoni, Washington Post, February 11, 2019
- “As vague as it is, the Green New Deal could have a real impact on Corporate America. Here’s Why,” Viktor Reklaitis, Market Watch from The Wall Street Journal, February 8, 2019
- “The Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez ‘Green New Deal’ Wants to Get Rid of Nuclear Power. That’s a Great Idea. – Nuclear power is simply too risky and complicated to supply our country’s energy,” Avery Thompson, Popular Mechanics, February 8, 2019
- “A Green New Deal is the infrastructure plan we need to be thinking about,” Tom Toles, Washington Post Opinion, December 5, 2018
- “How to Design a Green New Deal that Isn’t Over the Top,” Noah Smith, Bloomberg Opinion, February 12, 2019 (a very good critique, advancing the conversation)

Tom Toles in the Washington Post, June 18, 2018.
Spread the word; friends don't allow friends to repeat history.






 Posted by Ed Darrell
Posted by Ed Darrell 




/arc-anglerfish-arc2-prod-tronc.s3.amazonaws.com/public/QCCDQF6OBQ5ZTK37HYFDQF6AG4.jpg)